Suppress error messages about invalid or unconvertible characters are omitted. The iconv program converts the encoding of characters in inputfile from one coded character set to another. The result is written to standard output unless otherwise specified by the -output option. There are three main implementations of iconv in use. Linux's C runtime glibc contains one. Several platforms supply GNU libiconv, including macOS, FreeBSD and Cygwin, in some cases with additional encodings. On Windows we use a version of Yukihiro Nakadaira's winiconv, which is based on Windows' codepages. (We have added many encoding names for compatibility with other systems.). Download 201 vector icons and icon kits.Available in PNG, ICO or ICNS icons for Mac for free use. Folder Icon Maker is a Shareware icon utility tool that can be used to combine Mac OS X Finder icons. To use the program, simply drop an icon for the backdrop onto the view in the upper left. Mac OS X Manual Page For iconvopen (3) ICONVOPEN (3) Linux Programmer's Manual ICONVOPEN (3) NAME iconvopen - allocate descriptor for character set conversion SYNOPSIS #include iconv.h iconvt iconvopen (const char. tocode, const char. fromcode ); DESCRIPTION The iconvopen function allocates a conversion descriptor suitable for converting byte sequences from character encoding.
libiconv
Introduction to libiconv
International text is mostly encoded inUnicode.For historical reasons, however, it is sometimes still encoded using alanguage or country dependent character encoding. With the advent of theinternet and the frequent exchange of text across countries - even theviewing of a web page from a foreign country is a 'text exchange' in thiscontext -, conversions between these encodings have become a necessity.In particular, computers with the Windows operating system still operatein locale with a traditional (limited)character encoding. Some programs, like mailers and web browsers, mustbe able to convert between a given text encoding and the user's encoding.Other programs internally store strings in Unicode, to facilitate internalprocessing, and need to convert between internal string representation(Unicode) and external string representation (a traditional encoding)when they are doing I/O. GNU libiconv is a conversion library for bothkinds of applications.
Details
This library provides aniconv() implementation, for use on systems whichdon't have one, or whose implementation cannot convert from/to Unicode.It provides support for the encodings:
- European languages
- ASCII, ISO-8859-{1,2,3,4,5,7,9,10,13,14,15,16}, KOI8-R, KOI8-U, KOI8-RU, CP{1250,1251,1252,1253,1254,1257}, CP{850,866,1131}, Mac{Roman,CentralEurope,Iceland,Croatian,Romania}, Mac{Cyrillic,Ukraine,Greek,Turkish}, Macintosh
- Semitic languages
- ISO-8859-{6,8}, CP{1255,1256}, CP862, Mac{Hebrew,Arabic}
- Japanese
- EUC-JP, SHIFT_JIS, CP932, ISO-2022-JP, ISO-2022-JP-2, ISO-2022-JP-1, ISO-2022-JP-MS
- Chinese
- EUC-CN, HZ, GBK, CP936, GB18030, EUC-TW, BIG5, CP950, BIG5-HKSCS, BIG5-HKSCS:2004, BIG5-HKSCS:2001, BIG5-HKSCS:1999, ISO-2022-CN, ISO-2022-CN-EXT
- Korean
- EUC-KR, CP949, ISO-2022-KR, JOHAB
- Armenian
- ARMSCII-8
- Georgian
- Georgian-Academy, Georgian-PS
- Tajik
- KOI8-T
- Kazakh
- PT154, RK1048
- Thai
- ISO-8859-11, TIS-620, CP874, MacThai
- Laotian
- MuleLao-1, CP1133
- Vietnamese
- VISCII, TCVN, CP1258
- Platform specifics
- HP-ROMAN8, NEXTSTEP
- Full Unicode
- UTF-8
UCS-2, UCS-2BE, UCS-2LE
UCS-4, UCS-4BE, UCS-4LE
UTF-16, UTF-16BE, UTF-16LE
UTF-32, UTF-32BE, UTF-32LE
UTF-7
C99, JAVA - Full Unicode, in terms of
uint16_toruint32_t(with machine dependent endianness and alignment) - UCS-2-INTERNAL, UCS-4-INTERNAL
- Locale dependent, in terms of `char' or `wchar_t' (with machine dependent endianness and alignment, and with OS and locale dependent semantics)
- char, wchar_t
The empty encoding name ' is equivalent to 'char': it denotes the locale dependent character encoding.
--enable-extra-encodings, it also providessupport for a few extra encodings:- European languages
- CP{437,737,775,852,853,855,857,858,860,861,863,865,869,1125}
- Semitic languages
- CP864
- Japanese
- EUC-JISX0213, Shift_JISX0213, ISO-2022-JP-3
- Chinese
- BIG5-2003 (experimental)
- Turkmen
- TDS565
- Platform specifics
- ATARIST, RISCOS-LATIN1
It has also some limited support for transliteration, i.e. when a charactercannot be represented in the target character set, it can be approximatedthrough one or several similarly looking characters. Transliteration isactivated when '//TRANSLIT' is appended to the target encoding name.
libiconv is for you if your application needs to support multiple characterencodings, but that support lacks from your system.

Installation
As usual for GNU packages:Iconv Euc Utf
After installing GNU libiconv for the first time, it is recommended torecompile and reinstall GNU gettext, so that it can take advantage oflibiconv.
On systems other than GNU/Linux, the iconv program will be internationalizedonly if GNU gettext has been built and installed before GNU libiconv. Thismeans that the first time GNU libiconv is installed, we have a circulardependency between the GNU libiconv and GNU gettext packages, which can beresolved by building and installing either
- first libiconv, then gettext, then libiconv again,
- first gettext, then libiconv, then gettext again.
This library can be built and installed in two variants:
- The library mode. This works on all systems, and uses a library
libiconv.soand a header file<iconv.h>. (Both are installed through 'make install'.)To use it, simply
#include <iconv.h>and use the functions.To use it in an autoconfiguring package:
- If you don't use automake, append
m4/iconv.m4to youraclocal.m4file. - If you do use automake, add
m4/iconv.m4to your m4 macro repository. - Add to the link command line of libraries and executables that use the functions the placeholder
@LIBICONV@(or, if using libtool for the link,@LTLIBICONV@). If you use automake, the right place for these additions are the *_LDADD variables.
iconv.m4is also part of the GNU gettext package, which installs it in/usr/local/share/aclocal/iconv.m4. - If you don't use automake, append
- The libc plug/override mode. This works on GNU/Linux, Solaris and OSF/1 systems only. It is a way to get good iconv support without having glibc-2.1. It installs a library
preloadable_libiconv.so. This library can be used with LD_PRELOAD, to override the iconv* functions present in the C library.- On GNU/Linux and Solaris:
- On OSF/1:
Copyright
The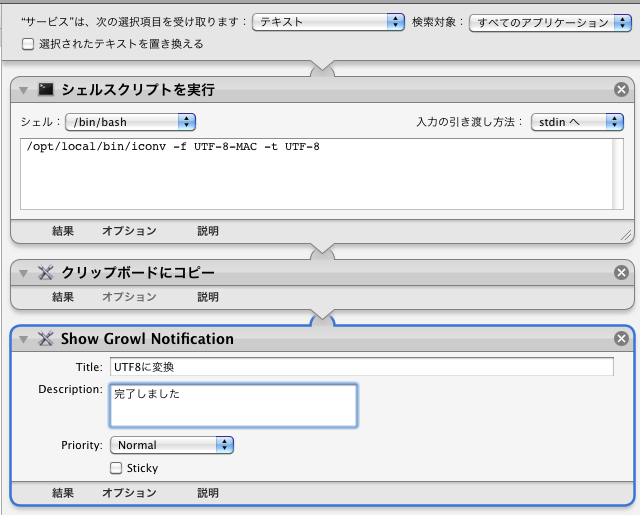
libiconv and libcharsetlibraries and their header files are under LGPL.The iconvprogram is under GPL.
Downloading libiconv
libiconv can be downloaded from https://ftp.gnu.org/pub/gnu/libiconv/libiconv-1.16.tar.gz.For other ways to obtain libiconv, please readHow to get GNU Software.The latest development sources can be obtained through thesavannah project.
Documentation
Below are the links for the online documentation.- The
iconvprogram - iconv.1.html
- The library functions
- iconv_open.3.html
iconv.3.html
iconv_close.3.html
iconvctl.3.html
iconv_open_into.3.html
Bug reports
Bug reports should be sent to<bug-gnu-libiconv
@gnu.org>.Return to GNU's home page.Please send general FSF & GNU inquiries to<gnu@gnu.org>.There are also other ways to contact the FSF.
Please send broken links and other corrections or suggestions to<bug-gnu-libiconv@gnu.org>.
Copyright (C) 1998, 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
Verbatim copying and distribution of this entire article ispermitted in any medium, provided this notice is preserved.
Last updated:$Date: 2019/05/09 00:50:43 $ $Author: haible $
Encode::UTF8Mac - 'utf-8-mac' a variant utf-8 used by OSX filesystem
Encode::UTF8Mac provides a encoding named 'utf-8-mac'.
On OSX, utf-8 encoding is used and it is NFD (Normalization Form canonical Decomposition) form. If you want to get NFC (Normalization Form canonical Composition) character you need to use Unicode::Normalize's NFC().
However, OSX filesystem does not follow the exact specification. Specifically, the following ranges are not decomposed.
iconv (bundled Mac) can use this encoding as 'utf-8-mac'.
This module adds same name 'utf-8-mac' encoding for Encode, it encode/decode text with that rule in mind. This will help when you decode file name on Mac.

See more information and Japanese example:
Encode::decode('utf-8-mac', $octets)
Decode as utf-8, and normalize form C except special range using Unicode::Normalize.
Encode::encode('utf-8-mac', $string)
Normalize form D except special range using Unicode::Normalize, and encode as utf-8.
OSX file system change NFD automatically. So actually, this is not necessary.
Icon For Microscope
If you are using Encode::Locale, you may want to do this.
Encode::Locale - provides useful 'magic' encoding.
Unicode::Normalize::Mac - this module uses it internally.
Naoki Tomita <tomita@cpan.org>
Icon For Mac Mail
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the same terms as Perl itself.
Iconv Mac Terminal
To install Encode::UTF8Mac, copy and paste the appropriate command in to your terminal.
For more information on module installation, please visit the detailed CPAN module installation guide.